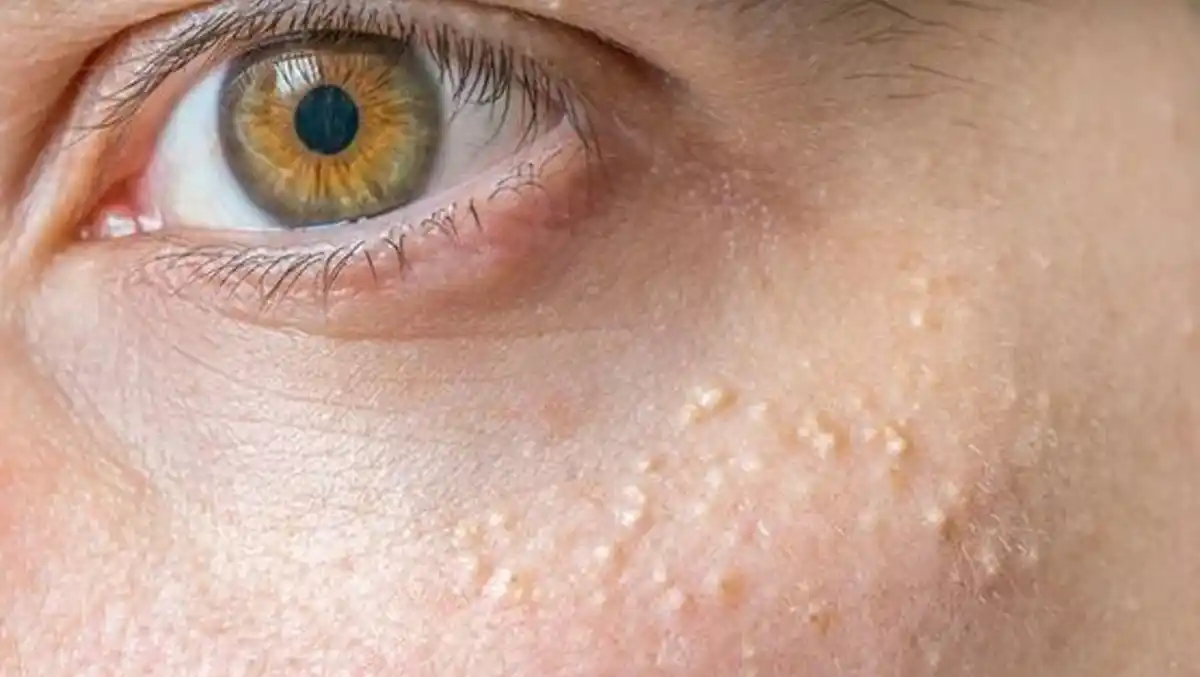
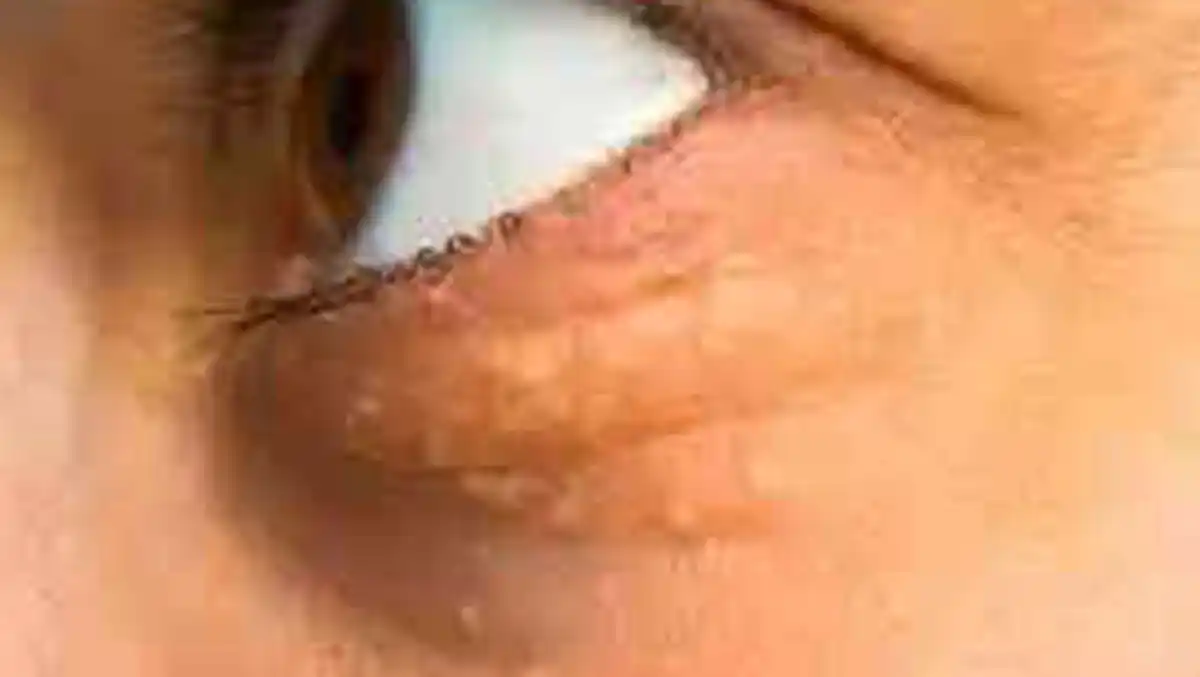
Xanthelasma is a condition characterized by the appearance of yellowish, fatty deposits around the eyes, often on the upper or lower eyelids. These deposits are caused by the buildup of cholesterol-rich material beneath the skin and are usually benign but may indicate an underlying lipid imbalance. Xanthelasma can be cosmetically bothersome and, in some cases, may grow larger over time. Excision surgery is an effective treatment for removing xanthelasma and restoring a smoother appearance to the eyelids.
Yellowish Plaques: The primary symptom of xanthelasma is the development of soft, yellowish plaques or bumps near the inner corners of the eyes, often symmetrical on both eyelids.
Painless: Xanthelasma typically does not cause pain or discomfort. However, the presence of these plaques can be visually unappealing and may affect a person's self-confidence.
Slow Growth: Over time, these deposits may increase in size, becoming more prominent, though they usually remain localized to the eyelid area.
Underlying Cholesterol Issues: While xanthelasma itself is not harmful, it may be associated with high cholesterol or lipid disorders in some individuals. Blood tests are often recommended to check for these underlying issues.
Xanthelasma removal through excision surgery is a safe and effective way to eliminate the yellowish plaques around the eyes, offering both cosmetic improvement and relief from any associated concerns. While the procedure can provide excellent results, managing underlying cholesterol issues is crucial to reducing the risk of recurrence. With proper care and follow-up, patients can enjoy smoother, clearer skin around the eyes and greater confidence in their appearance. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider for the best treatment approach tailored to your specific condition.